Scanning lockdown¶
Now that we can create and scan custom variables, we can write a proper lockdown iterator that enables us to explore different scenarios.
Create a file called lockdown.inp and copy in the below;
# Full lockdown (red)
.scale_rate[0] = 0.05
.can_work[0] = False
# Relaxed lockdown (yellow)
.scale_rate[1] = 0.1
.can_work[1] = False
# More relaxed lockdown (green)
.scale_rate[2] = 0.1
.can_work[2] = True
This has defined three lockdown states, ranging from “red” (full lockdown with strong reduction in transmission rate and working) to “green” (relaxed lockdown with weaker reduction in transmission rate and work allowed).
To use this data create an iterator in a file called lockdown.py and
copy in the below;
from metawards.iterators import advance_infprob, advance_fixed, \
advance_play, iterate_working_week
def get_lockdown_state(population):
if not hasattr(population, "lockdown_state"):
population.lockdown_state = -1
population.is_locked_down = False
if population.total > 5000:
if population.lockdown_state == -1:
print(f"Lockdown started on {population.date}")
population.lockdown_state = 0
population.is_locked_down = True
elif population.lockdown_state > 0:
print(f"Restarting lockdown on {population.date}")
population.lockdown_state = 0
population.is_locked_down = True
elif population.total > 3000:
if population.lockdown_state == 2:
print(f"Re-entering relaxed (yellow) on {population.date}")
population.lockdown_state = 1
elif population.total < 2000:
if population.lockdown_state == 0:
print(f"Entering relaxed (yellow) on {population.date}")
population.lockdown_state = 1
elif population.total < 1000:
if population.lockdown_state == 1:
print(f"Entering relaxed (green) on {population.date}")
population.lockdown_state = 2
return population.lockdown_state
def advance_lockdown(network, population, **kwargs):
params = network.params
state = get_lockdown_state(population)
scale_rate = params.user_params["scale_rate"][state]
can_work = params.user_params["can_work"][state]
print(f"Lockdown {state}: scale_rate = {scale_rate}, can_work = {can_work}")
advance_infprob(scale_rate=scale_rate,
network=network, population=population,
**kwargs)
advance_play(network=network, population=population,
**kwargs)
if can_work:
advance_fixed(network=network, population=population,
**kwargs)
def iterate_custom(network, population, **kwargs):
params = network.params
state = get_lockdown_state(population)
if population.is_locked_down:
print("Locked down")
return [advance_lockdown]
else:
print("Normal working week day")
return iterate_working_week(network=network,
population=population,
**kwargs)
The get_lockdown_state function is the most complex and different.
It uses the number of infecteds (population.total) to decide which
lockdown_state should be used. This is an integer, with -1
meaning no lockdown, 0 being “red”, 1 “yellow” and 2 “green”.
Whether or not the population is locked down is stored in the
population.is_locked_down variable. If this is “False” then
iterate_lockdown simply returns the result of
iterate_working_week(). Otherwise,
it returns the advance_lockdown function that we’ve defined.
This advance_lockdown function obtains the scale_rate and
can_work custom user parameters from the
Parameters objects in the model
Network.
It calls advance_infprob() with
the set scale_rate scaling factor, before calling
advance_play(), and then, if
can_work is “True”, advance_fixed().
Run metawards using the below commands and see what you get;
metawards -d lurgy3 -a ExtraSeedsLondon.dat -u lockdown.inp --iterator lockdown
metawards-plot -i output/results.csv.bz2
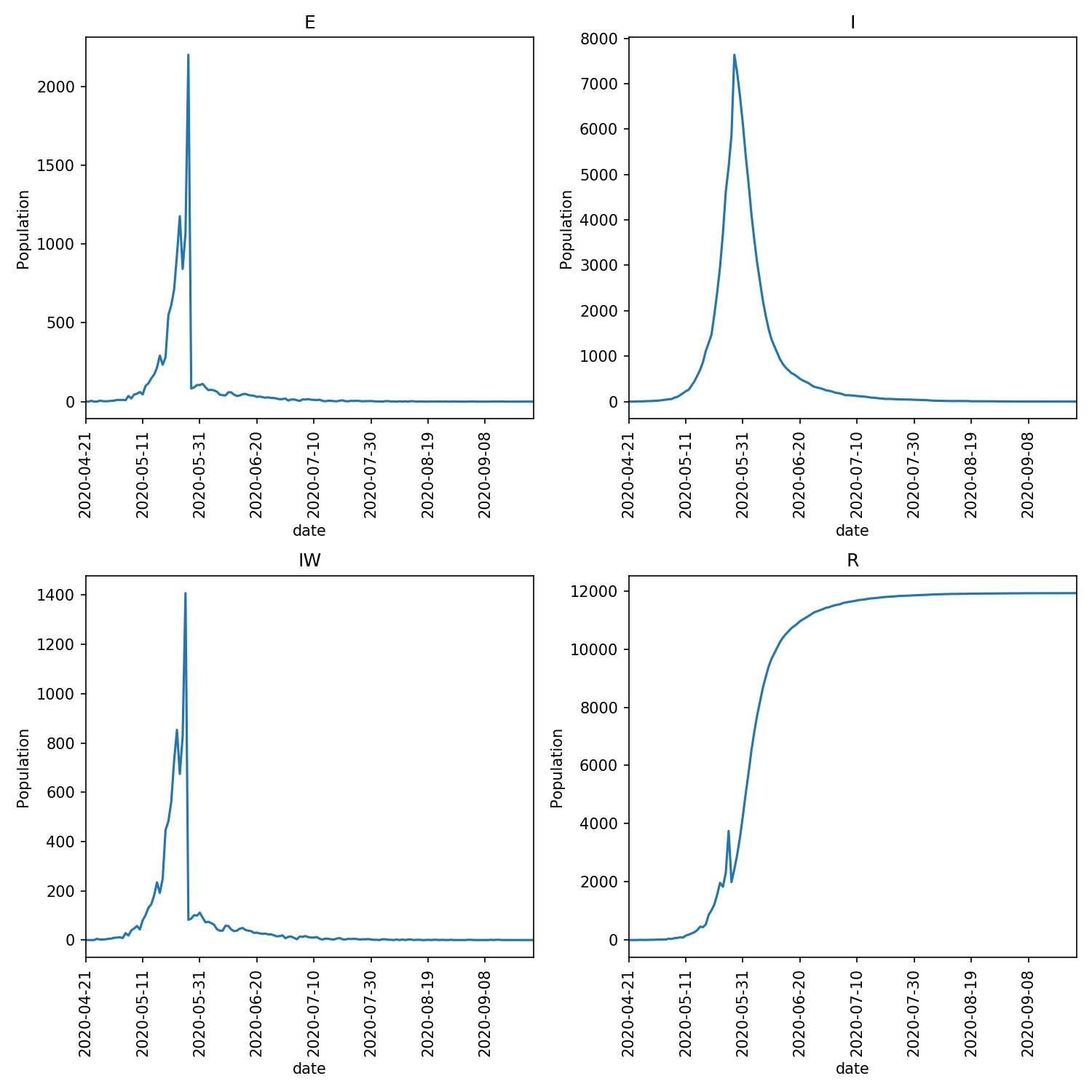
I see;
33 4880
S: 56074296 E: 842 I: 4625 R: 2314 IW: 827 TOTAL POPULATION 56081235
Normal working week day
34 5467
S: 56072094 E: 1071 I: 5163 R: 3749 IW: 1408 TOTAL POPULATION 56081006
Lockdown started on 2020-05-26
Locked down
Lockdown 0: scale_rate = 0.05, can_work = 0.0
35 6234
S: 56072011 E: 2202 I: 5873 R: 1991 IW: 82 TOTAL POPULATION 56079875
Locked down
Lockdown 0: scale_rate = 0.05, can_work = 0.0
...
46 2700
S: 56071140 E: 44 I: 2221 R: 8672 IW: 38 TOTAL POPULATION 56082033
Locked down
Lockdown 0: scale_rate = 0.05, can_work = 0.0
47 2265
S: 56071101 E: 41 I: 1889 R: 9046 IW: 38 TOTAL POPULATION 56082036
Entering relaxed (yellow) on 2020-06-08
Locked down
Lockdown 1: scale_rate = 0.1, can_work = 0.0
48 1930
S: 56071042 E: 39 I: 1601 R: 9395 IW: 58 TOTAL POPULATION 56082038
Locked down
Lockdown 1: scale_rate = 0.1, can_work = 0.0
...
52 1121
S: 56070864 E: 36 I: 933 R: 10244 IW: 38 TOTAL POPULATION 56082041
Entering relaxed (green) on 2020-06-13
Locked down
Lockdown 2: scale_rate = 0.1, can_work = 1.0
with the overview graph as here;
Running on a cluster¶
Now that this is working, we can scan through lots of different lockdown
scenarios by creating an input file that varies the scale_rate and
can_work parameters. Create an input file called scan.csv and
copy in the following;
# Adjust "red" state from 0.05 to 0.20
# while adjusting "yellow" from "green" + 0.05 to 0.25
# while adjusting "green" from "yellow" if working, or
# "yellow" + 0.05 if not
.scale_rate[0] .scale_rate[1] .scale_rate[2] .can_work[2]
# first set allow working in "green"
0.05 0.10 0.10 True
0.05 0.15 0.15 True
0.05 0.20 0.20 True
0.05 0.25 0.25 True
0.10 0.15 0.15 True
0.10 0.20 0.20 True
0.10 0.25 0.25 True
0.15 0.20 0.20 True
0.15 0.25 0.25 True
0.20 0.25 0.25 True
# second set prevent working in "green"
0.05 0.10 0.15 False
0.05 0.15 0.20 False
0.05 0.20 0.25 False
0.05 0.25 0.30 False
0.10 0.15 0.20 False
0.10 0.20 0.25 False
0.10 0.25 0.30 False
0.15 0.20 0.25 False
0.15 0.25 0.30 False
0.20 0.25 0.30 False
Note
Note that we have added comments to this file using ‘#’ - these are useful to help your future self understand what you were doing
Copy all of the files onto a cluster and submit the job where you repeat each adjustable variable set 16 times. I used the PBS job script;
#!/bin/bash
#PBS -l walltime=12:00:00
#PBS -l select=4:ncpus=64:mem=64GB
# The above sets 4 nodes with 64 cores each
# source the version of metawards we want to use
source $HOME/envs/metawards-0.8.0/bin/activate
# change into the directory from which this job was submitted
cd $PBS_O_WORKDIR
metawards --additional ExtraSeedsLondon.dat \
--disease lurgy3 -u lockdown.inp \
--iterator lockdown \
--input scan.csv --repeats 16 --nthreads 8 \
--force-overwrite-output
Submit your job (e.g. qsub jobscript.sh) and then wait for it to
finish. Once it has completed, generate the overview and average
graphs via;
metawards-plot -i output/results.csv.bz2
metawards-plot --animate output/overview*.jpg
metawards-plot --animate output/average*.jpg
What do you see?
I get a range of scenarios, from outbreaks that are controlled until they die out, through oscillating outbreaks where the population is forever moved between the “green” and “yellow” lockdown states, through to outbreaks that grow despite lockdown. These can all be seen here;
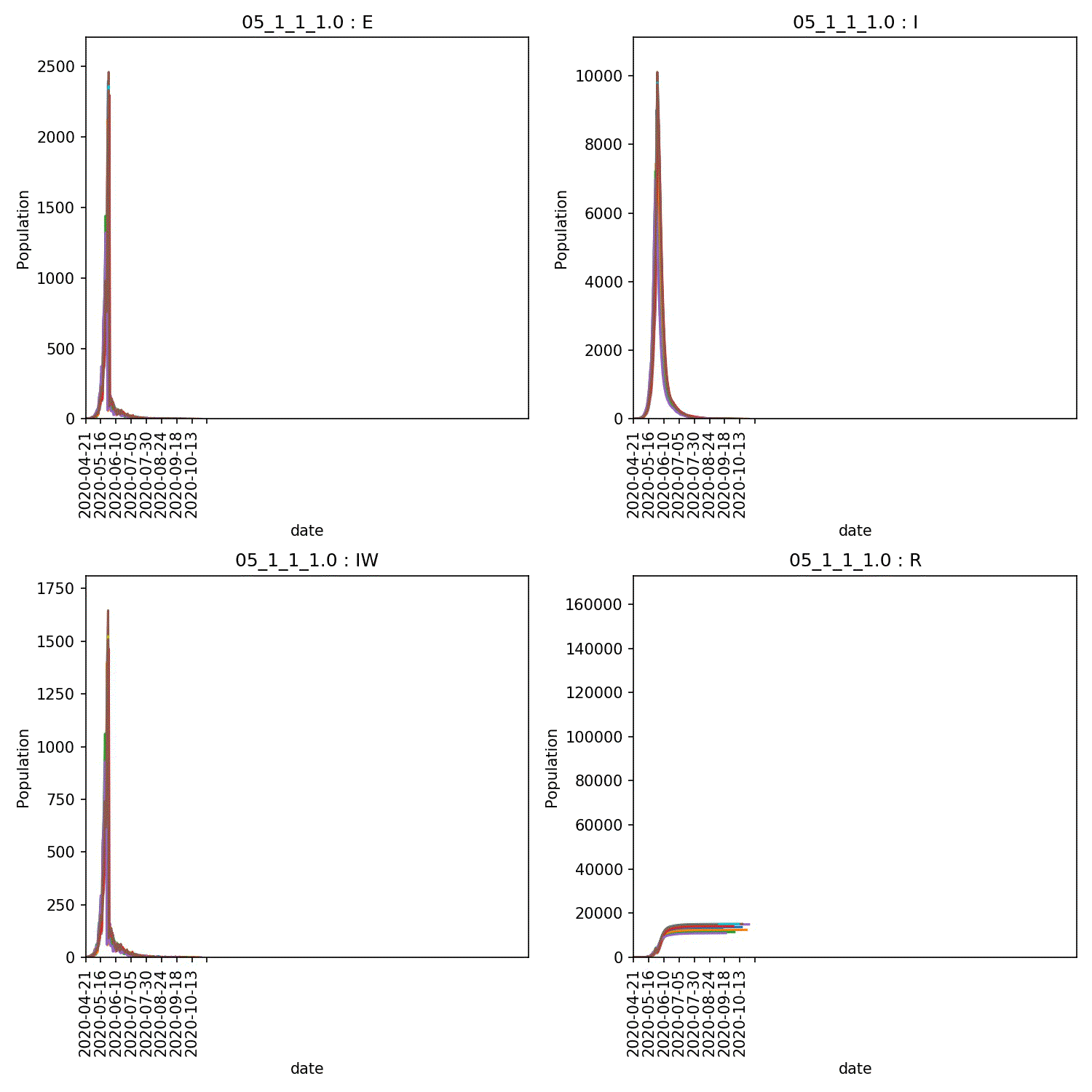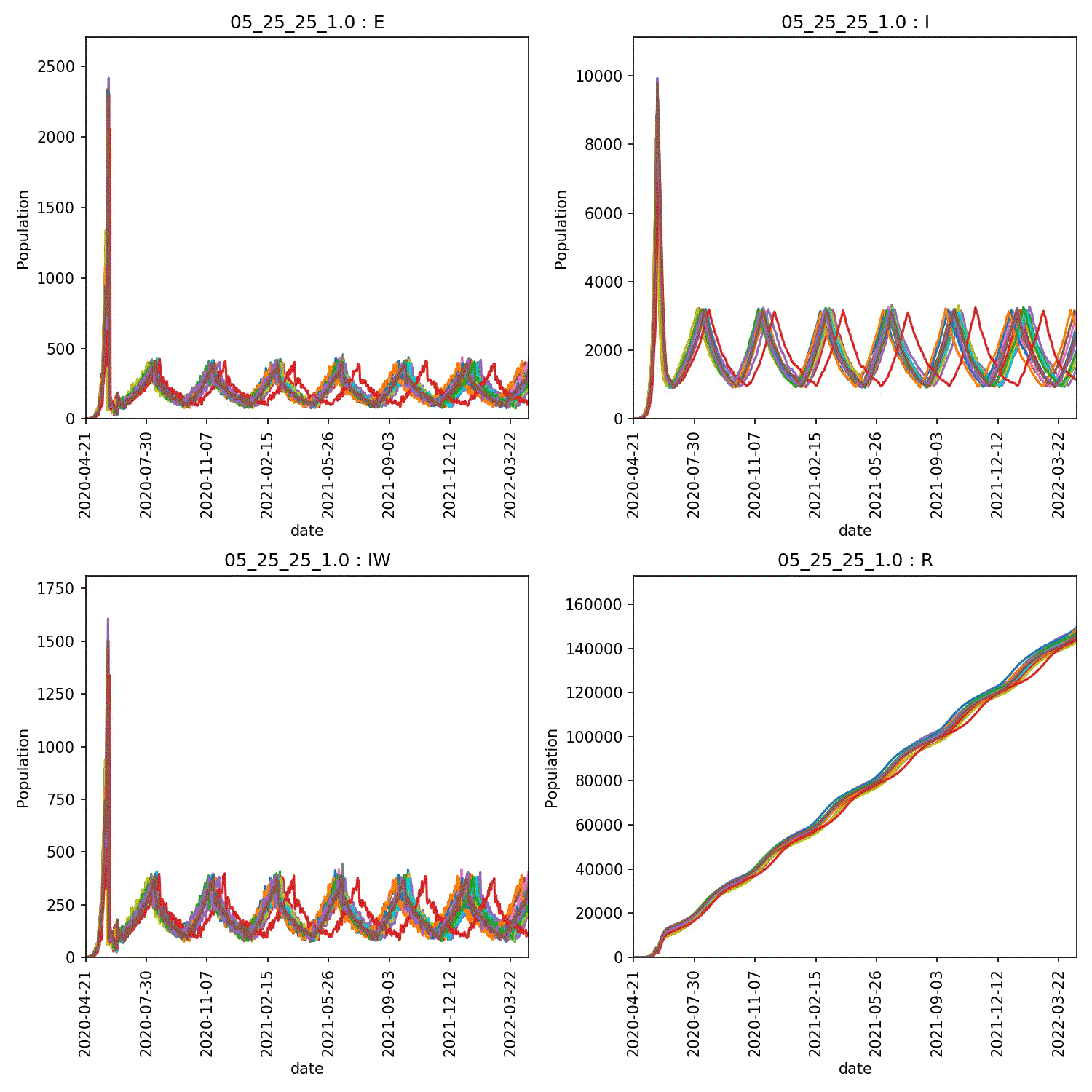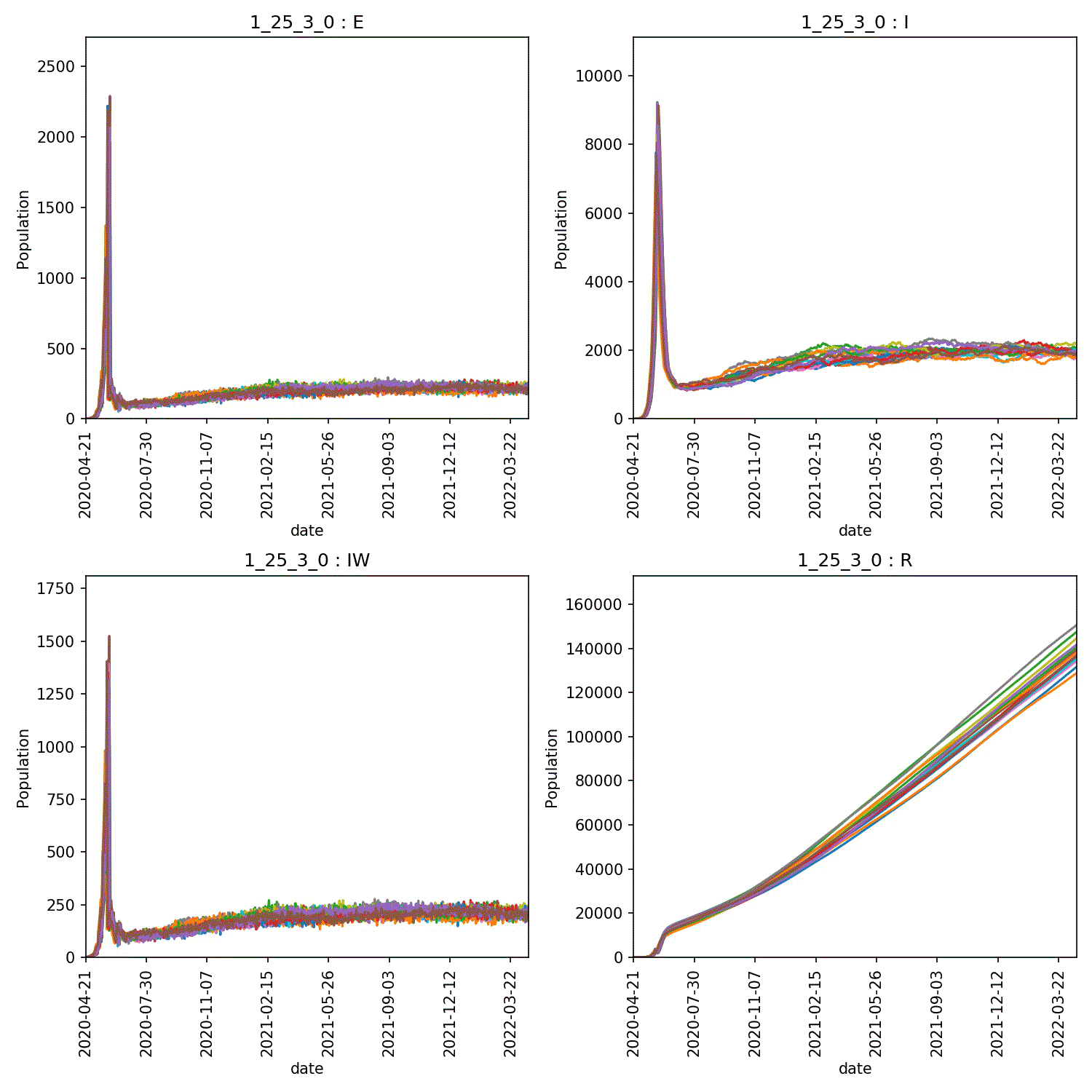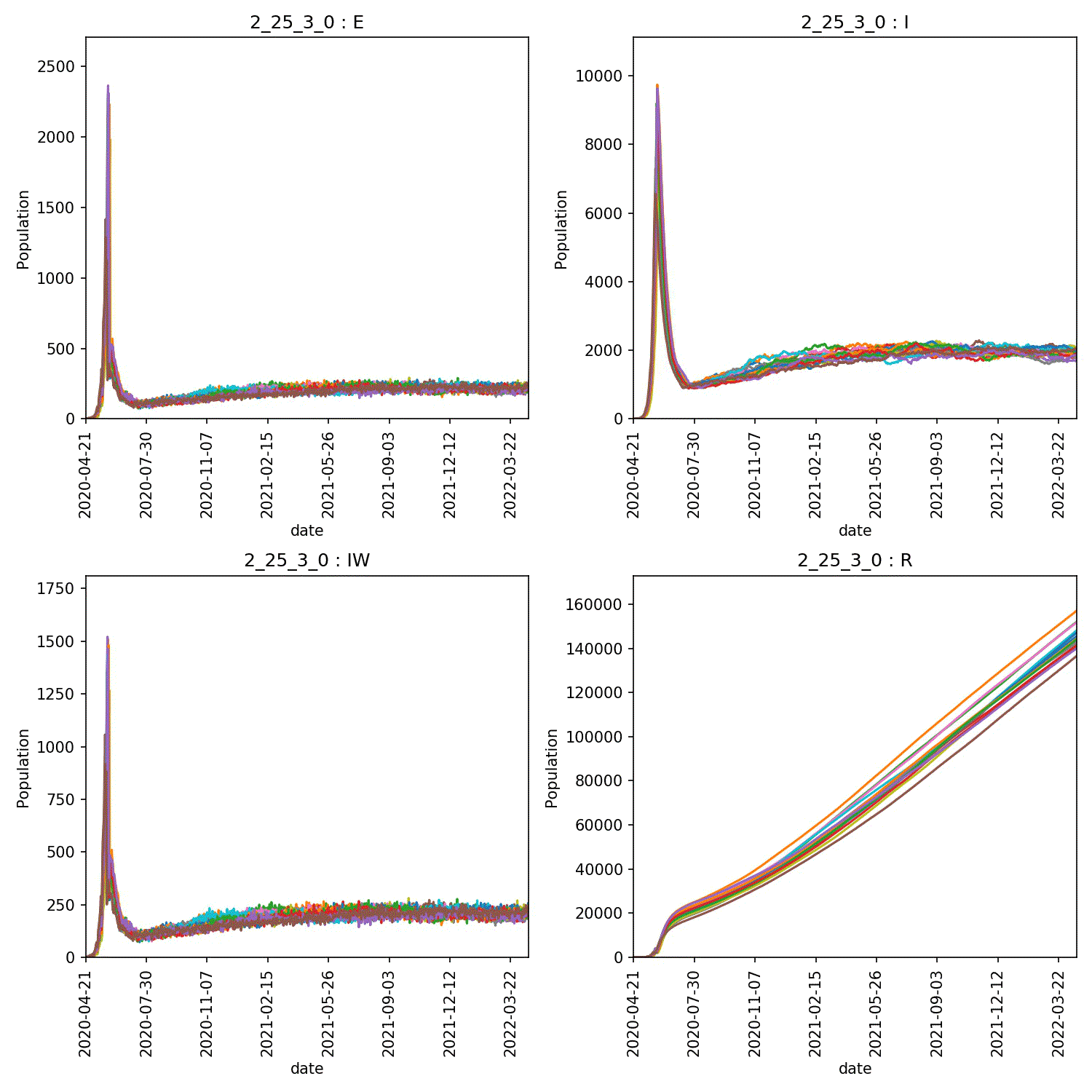
Moving beyond this simple demo¶
This was a simple demo of how different lockdown scenarios could be modelled using custom parameters and custom iterators.
You can of course go further, e.g. by using your custom advance function
to change actual parameters of the model or of the disease. Feel
free to change any of the parameters in
network.params or
network.params.disease_params directly.
You could, for example, reduce the
network.params.dyn_dist_cutoff
variable as lockdown starts. Or you could directly adjust
network.params.disease_params.beta[0].
You can also add these parameters to your scan of adjustable parameters. The full list of built-in adjustable parameters is below;
UV:
Adjust the Parameters.UV parameter
beta:
Adjust the Disease.beta parameter
contrib_foi:
Adjust the Disease.contrib_foi parameter
daily_imports:
Adjust the Parameters.daily_imports parameter
daily_ward_vaccination_capacity:
Adjust the Parameters.daily_ward_vaccination_capacity
parameter
data_dist_cutoff:
Adjust the Parameters.data_dist_cutoff parameter
dyn_dist_cutoff:
Adjust the Parameters.dyn_dist_cutoff parameter
dyn_play_at_home:
Adjust the Parameters.dyn_play_at_home parameter
global_detection_thresh:
Adjust the Parameters.global_detection_thresh parameter
initial_inf:
Adjust the Parameters.initial_inf parameter
length_day:
Adjust the Parameters.length_day parameter
local_vaccination_thesh:
Adjust the Parameters.local_vaccination_thresh parameter
neighbour_weight_threshold:
Adjust the Parameters.neighbour_weight_threshold parameter
play_to_work:
Adjust the Parameters.play_to_work parameter
plength_day:
Adjust the Parameters.plength_day parameter
progress:
Adjust the Disease.progress parameter
static_play_at_home:
Adjust the Parameters.static_play_at_home parameter
too_ill_to_move:
Adjust the Disease.too_ill_to_move parameter
user:
Adjust a custom user-supplied parameter, held in
Parameters.user_params[name]. Set a user parameter
called 'name' via 'user.name' or '.name'.
work_to_play:
Adjust the Parameters.work_to_play parameter