Modelling vaccination
Let’s now use MoveGenerator and
go_ward() to model vaccination.
First, we will create a new version of the lurgy that includes a vaccination stage. To do this in Python open ipython or jupyter and type;
>>> from metawards import Disease
>>> lurgy = Disease("lurgy5")
>>> lurgy.add("E", beta=0.0, progress=1.0)
>>> lurgy.add("I1", beta=0.4, progress=0.2)
>>> lurgy.add("I2", beta=0.5, progress=0.5, too_ill_to_move=0.5)
>>> lurgy.add("I3", beta=0.5, progress=0.8, too_ill_to_move=0.8)
>>> lurgy.add("R")
>>> lurgy.add("V", beta=0.0, progress=0.0, is_infected=False)
>>> lurgy.to_json("lurgy5.json", indent=2, auto_bzip=False)
or, in R/RStudio type;
> library(metawards)
> lurgy <- metawards$Disease("lurgy5")
> lurgy$add("E", beta=0.0, progress=1.0)
> lurgy$add("I1", beta=0.4, progress=0.2)
> lurgy$add("I2", beta=0.5, progress=0.5, too_ill_to_move=0.5)
> lurgy$add("I3", beta=0.5, progress=0.8, too_ill_to_move=0.8)
> lurgy$add("R")
> lurgy$add("V", beta=0.0, progress=0.0, is_infected=FALSE)
> lurgy$to_json("lurgy5.json", indent=2, auto_bzip=FALSE)
or, simply copy the below into the file lurgy5.json;
{
"name": "lurgy5",
"stage": ["E", "I1", "I2", "I3", "R", "V"],
"mapping": ["E", "I", "I", "I", "R", "V"],
"beta": [0.0, 0.4, 0.5, 0.5, 0.0, 0.0],
"progress": [1.0, 0.2, 0.5, 0.8, 0.0, 0.0],
"too_ill_to_move": [0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 0.8, 0.0, 0.0],
"contrib_foi": [1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
"is_infected": [true, true, true, true, false, false],
"start_symptom": 2
}
This has added an extra stage, called V, which is used to hold
vaccinated individuals. Because vaccinated individuals are
not infected, we have to set is_infected to false for
this stage (note how this is set automatically for the R stage).
Also, once vaccinated, individuals will remain in the V stage. Thus
progress for this stage is set to 0.0, just like it is
automatically set for the R stage.
We can run a quick test of this model using;
metawards -d lurgy5.json -m single -a 5
This uses the single-ward model and infects 5 individuals on day 1 with
the disease described in lurgy5.json.
You should see that the outbreak progresses as before, with many of the 1000-strong population of the ward infected, and, currently, no-one vaccinated.
Vaccinating using go_ward
We can model vaccination by writing a mover that uses
go_ward to move up to 50 individuals per
day from S to V (e.g. representing a vaccination capacity of
50 vaccinations per day).
Do this by creating a file called move_vaccinate.py and copying
in the below;
from metawards.movers import MoveGenerator, go_ward
def move_vaccinate(**kwargs):
capacity = 50 # number of vaccinations per day
def go_vaccinate(**kwargs):
gen = MoveGenerator(from_stage="S", to_stage="V", number=capacity)
go_ward(generator=gen, **kwargs)
return [go_vaccinate]
Run the model using;
metawards -d lurgy5.json -m single -a 5 --mover move_vaccinate.py
You should see that the number of vaccinated individuals climbs by 50 each day. This reduces the number of susceptibles, meaning that the infection is dampened before it can get going.
Demand-driven vaccination
This model started vaccination on the first day of the outbreak. We
can instead trigger vaccination based on a threshold of infections,
e.g. because maybe the vaccine has a limited supply. Edit
move_vaccinate.py to add a trigger where vaccination starts
only when the number of infections grows above 100, e.g.
from metawards.movers import MoveGenerator, go_ward
from metawards.utils import Console
def move_vaccinate(**kwargs):
capacity = 50 # number of vaccinations per day
trigger = 100 # number of infections to trigger vaccination
def go_vaccinate(network, population, **kwargs):
params = network.params
# Are we vaccinating? If this has not been set then we are not
is_vaccinating = params.user_params.get("is_vaccinating", False)
if not is_vaccinating and population.total >= trigger:
# trigger vaccination
params.user_params["is_vaccinating"] = True
is_vaccinating = True
Console.info("Starting vaccination")
if is_vaccinating:
gen = MoveGenerator(from_stage="S", to_stage="V", number=capacity)
go_ward(generator=gen, network=network,
population=population, **kwargs)
return [go_vaccinate]
Run the model using;
metawards -d lurgy5.json -m single -a 5 --mover move_vaccinate.py
You should see now in the output that vaccination starts when the number of infections rises about 100, which for me happened on day 17. Vaccination of the remaining susceptibles completed by day 27, with the outbreak ending with 528 vaccinated individuals and 472 who contracted the lurgy and recovered.
National vaccination
We can extend the model to vaccinate on a per-ward basis if the number
of infections climbs above a threshold in an individual ward. To do this,
modify move_vaccinate.py to read;
from metawards import WardID
from metawards.movers import MoveGenerator, go_ward
from metawards.utils import Console
def move_vaccinate(**kwargs):
capacity = 50 # number of vaccinations per day
trigger = 20 # number of infections to trigger vaccination
stop_trigger = 5 # number of infections to stop vaccination
def go_vaccinate(network, workspace, **kwargs):
# create ward-local is_vaccinating parameters, that defaults to 0.0
is_vaccinating = network.nodes.get_custom("is_vaccinating", 0.0)
vaccinate = []
I_in_wards = workspace.I_in_wards
for i in range(1, network.nnodes + 1):
if not is_vaccinating[i]:
if I_in_wards[i] >= trigger:
is_vaccinating[i] = 1.0
if is_vaccinating[i]:
if I_in_wards[i] < stop_trigger:
is_vaccinating[i] = 0.0
else:
vaccinate.append(WardID(i, all_commute=True))
vaccinate.append(WardID(i))
nv = int(sum(is_vaccinating))
if nv > 0:
print(f"Vaccinating in wards: number = {nv}")
gen = MoveGenerator(from_ward=vaccinate,
from_stage="S", to_stage="V", number=capacity)
go_ward(generator=gen, network=network,
workspace=workspace, **kwargs)
return [go_vaccinate]
You can run this model using;
metawards -d lurgy5.json -m 2011Data --mover move_vaccinate.py -a ExtraSeedsLondon.dat
In this case, vaccination starts in a ward if the number of infections grows to 50 or above. Then, there is capacity for 20 vaccinations per day per ward and per ward-link. If the number of infections in the ward drops below 5 then vaccination is stopped.
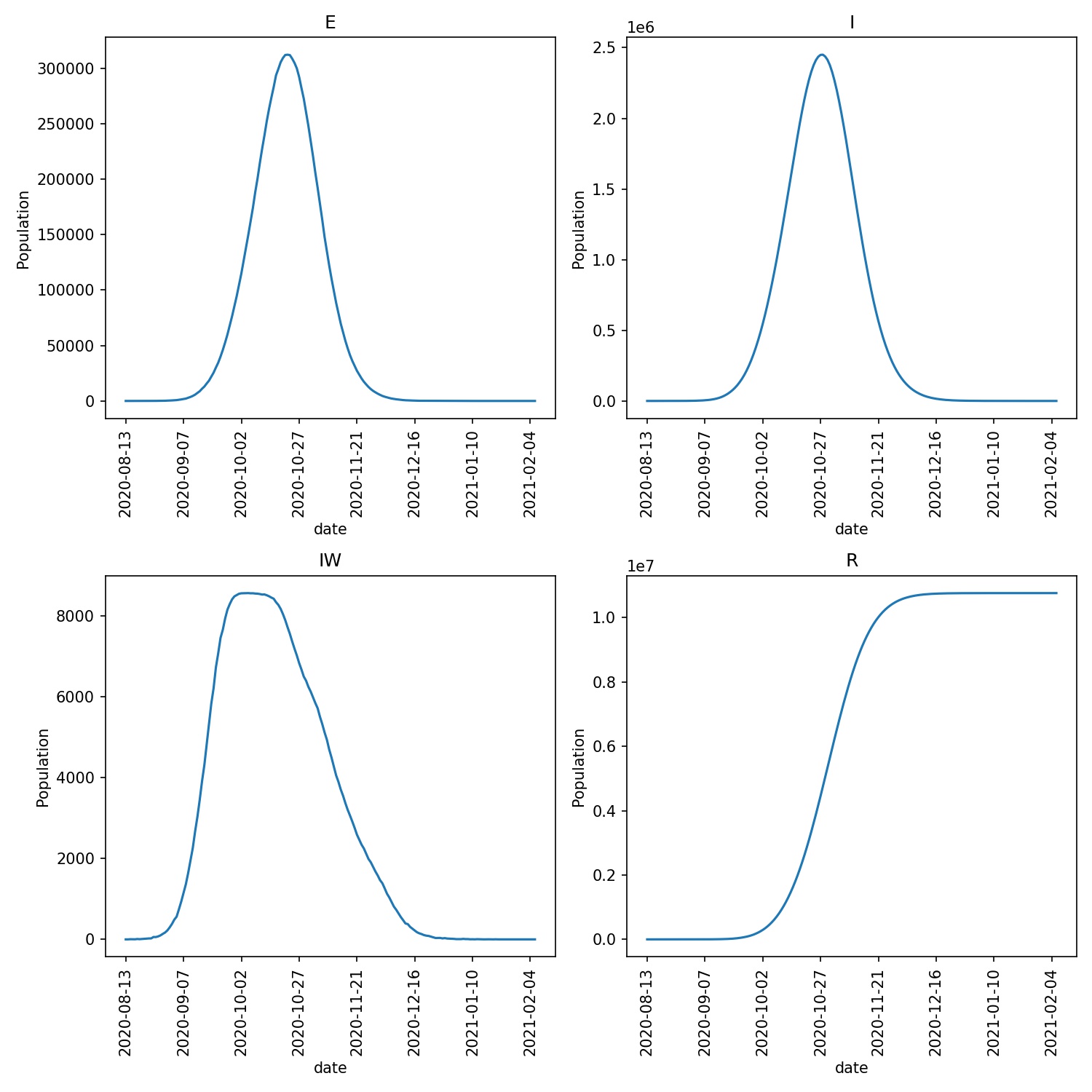
For my run, I see that all wards enter the vaccination program, with
eventually ~44 M vaccinations and ~10 M infections. The progress
plot produced via metawards-plot is shown below;