Where is the weekend?
It may not have escaped your attention that every day is a work day in this model. While this may seem unrealistic, we must remember that these are random, imperfect models, based on very noisy data. Adding more “realism” may be counter-productive, especially as modern working patterns mean that there is blurring of the line between work days and weekends.
This doesn’t mean that we can’t model a weekend. Indeed, metawards
is really flexible and you can customise exactly what is performed
for each model day.
Creating the weekend
Create a new directory called weekend and copy into it your
lurgy3.json disease parameters. Change into this directory and
create a new file called weekend.py, and copy into it the below
code.
from metawards.utils import Console
def iterate_weekend(**kwargs):
Console.print("Hello iterate_weekend")
return []
This is a simple function called iterate_weekend. It takes an
unspecified number of
keyword arguments (**kwargs)
(more about these later). It returns an empty list ([]). All it does
is print Hello iterate_weekend to the screen.
Note
Notice that you must print using the
Console.print function of
Console(). This ensures that all printing
goes to the right place and stays sane when multiple processes
and threads all try to print at the same time. It also ensures
that everything that is printed to the screen also gets printed
to a file for safekeeping (output/console.log.bz2). It is
very important that information is not lost when running a job.
You can run this function by starting ipython in this directory
and typing;
In [1]: import weekend
In [2]: weekend.iterate_weekend()
Hello iterate_weekend
Out[2]: []
You can tell metawards to call this function every iteration
using the --iterator command-line argument. Type;
metawards metawards -d lurgy3 --additional ExtraSeedsLondon.dat --iterator weekend
You should see a very different outbreak to what you have before, e.g.
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Day 0 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Hello iterate_weekend
S: 56082077 E: 0 I: 0 R: 0 IW: 0 POPULATION: 56082077
Number of infections: 0
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Day 1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Hello iterate_weekend
seeding play_infections[0][255] += 5
S: 56082072 E: 5 I: 0 R: 0 IW: 0 POPULATION: 56082077
Number of infections: 5
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Day 2 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Hello iterate_weekend
S: 56082072 E: 4 I: 1 R: 0 IW: 0 POPULATION: 56082077
Number of infections: 5
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Day 3 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Hello iterate_weekend
S: 56082072 E: 2 I: 3 R: 0 IW: 0 POPULATION: 56082077
Number of infections: 5
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Day 4 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Hello iterate_weekend
S: 56082072 E: 2 I: 2 R: 1 IW: 0 POPULATION: 56082077
Number of infections: 4
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Day 5 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Hello iterate_weekend
S: 56082072 E: 1 I: 2 R: 2 IW: 0 POPULATION: 56082077
Number of infections: 3
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Day 6 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Hello iterate_weekend
S: 56082072 E: 0 I: 2 R: 3 IW: 0 POPULATION: 56082077
Number of infections: 2
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Day 7 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Hello iterate_weekend
S: 56082072 E: 0 I: 1 R: 4 IW: 0 POPULATION: 56082077
Number of infections: 1
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Day 8 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
Hello iterate_weekend
S: 56082072 E: 0 I: 0 R: 5 IW: 0 POPULATION: 56082077
Number of infections: 0
Infection died ... Ending on day 9
What happened here? Well, just as you imported weekend into ipython
and called the iterate_weekend function, so too has metawards.
The --integrator option tells metawards to import the weekend
module. metawards then automatically found the first function in that
module whose name started with iterate, in this case iterate_weekend.
Then, metawards called this function for every iteration of the
model run.
You can name your function whatever you want, e.g. edit weekend.py
to read;
from metawards.utils import Console
def another_function(**kwargs):
Console.print("Hello another_function")
return []
def iterate_weekend(**kwargs):
Console.print("Hello iterate_weekend")
return []
This has added another function called another_function. You can tell
metawards to use this function using
--iterator weekend::another_function. Try running this using the
command below;
metawards -d lurgy3 --additional ExtraSeedsLondon.dat --iterator weekend::another_function
You should see Hello another_function is now printed for
every iteration.
Warning
Sometimes you may see metawards exit with a warning that it can’t
find your iterator function. This is likely because there is a typo
or syntax error in your iterator. metawards does its best to
detect these and report them to you, so check above the error in the
output to see if there is anything helpful. If not, then run your
iterator in python to see if you get any errors, e.g. if your iterator
is in a file called iterator.py then type python iterator.py.
If there is an error, then that will be printed to the screen.
Printing debug output
In general, you should only print things to the screen if they will be useful
for the user of the program. Sometimes when developing you want to print
some debugging output that can verify that everything is working. To do this,
using Console.debug. For example,
change your iterator to;
from metawards.utils import Console
def iterate_weekend(**kwargs):
Console.debug("Hello iterate_weekend")
return []
Now, you will only see this print output if the --debug option is passed
to metawards, e.g.
metawards -d lurgy2 --iterator weekend --debug
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Day 0 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
[15:23:08] Hello iterate_weekend weekend.py:5
S: 56082077 E: 0 I: 0 R: 0 IW: 0 POPULATION: 56082077
Number of infections: 0
Note that the time of the debug string, and the line and file of the debug
statement are included. You can also easily print the values of variables
using the variables keyword argument to
debug(), e.g.
from metawards.utils import Console
def iterate_weekend(**kwargs):
a = 42
b = "This is a string"
Console.debug("Hello iterate_weekend", variables=[a, b])
return []
metawards -d lurgy2 --iterator weekend --debug
━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ Day 0 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━
[15:25:38] Hello iterate_weekend weekend.py:8
Name │ Value
══════╪══════════════════
a │ 42
b │ This is a string
More information about debug strings, debugging levels, and how you can leave these debug strings in production code is available here.
Advancing the outbreak
You may have noticed that the disease outbreak was not advancing during any of the runs using your custom weekend iterator. The output showed that five initial infections were seeded. These progressed through the disease stages until all five individuals moved into the R state.
The reason the disease hasn’t advanced is because you haven’t supplied
any functions that are used to advance the outbreak. The job of
the iterator function is to return the functions that are needed to
advance an outbreak (so-called advance functions).
You can write an advance function by editing weekend.py to contain;
from metawards.iterators import advance_infprob, advance_play
from metawards.utils import Console
def iterate_weekend(**kwargs):
Console.debug("Hello iterate_weekend")
return [advance_infprob, advance_play]
In this code you have imported the advance_infprob()
and advance_play() advance functions.
These were described on the last page. By returning
them from iterate_weekend you have told metawards to call them,
one after another, to advance the outbreak. If you now run
metawards using this new weekend.py via;
metawards -d lurgy3 --additional ExtraSeedsLondon.dat --iterator weekend
you will see that the outbreak now advances throughout the population.
However, each day now only progresses new infections using the “play” mode
advance_play(). The “work” mode
advance_fixed(), is not used, meaning
that every day is now modelled as like a weekend.
Create an overview graph of your “weekend only” run and compare it to the results from the “weekday only” runs in part 2. Do you see a difference?
My graph is shown below;
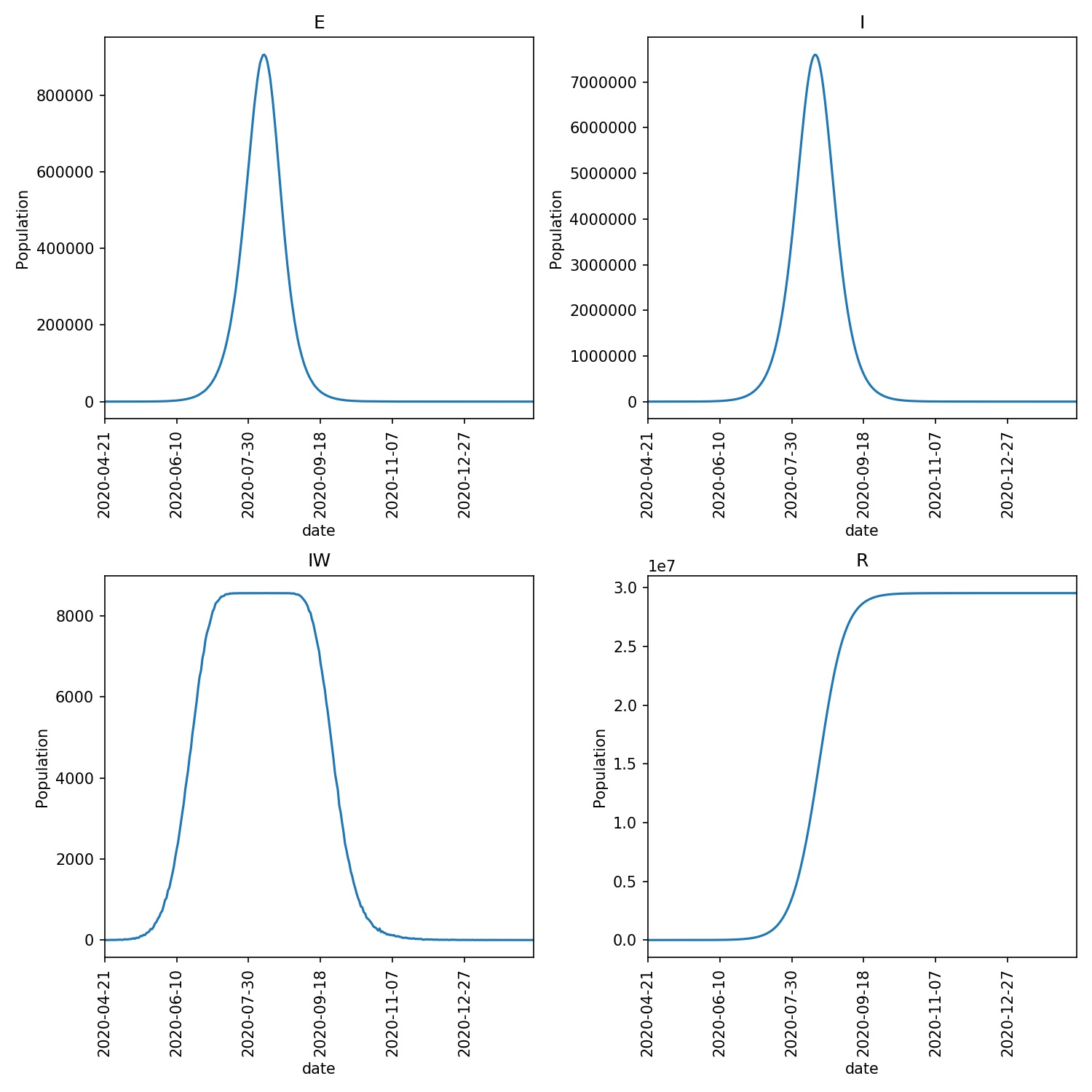
It is clear that the outbreak is now much smaller, peaking at 7 million as opposed to nearly 20 million. The peak is also broadened out, with the outbreak lasting months rather than weeks.
Changing iterators with time
A week of only weekends is also not realistic. We can however create a function that can choose which advance functions to return based on the day of the outbreak.
To do this, create a new python file called week.py and copy into
it the code below;
from metawards.iterators import advance_infprob, \
advance_fixed, \
advance_play
from metawards.utils import Console
def iterate_week(population, **kwargs):
date = population.date
Console.debug(f"Creating functions for {date}")
if date.weekday() < 5:
Console.debug("This is a weekday")
return [advance_infprob,
advance_fixed,
advance_play]
else:
Console.debug("This is a weekend")
return [advance_infprob,
advance_play]
This has created an iterate_week function. This has a slightly
different signature to iterate_weekend, in that it accepts
the population argument. Every iterator is passed a lot of
arguments, most of which are ignored by the **kwarg variables.
When you need an argument you name it in the function. In this case,
we need the population argument. This is a
Population object, which contains the distribution
of the population across the different S, E, I states,
plus the current date of the outbreak (
Population.date).
The date is a standard Python date object.
The .weekday() function returns a number from 0-6 to correspond
with Monday to Sunday (0 is Monday, 6 is Sunday).
If the weekday is less than 5, then the day must be a weekday. Hence
the iterate_week function returns the infprob, fixed and play
advance functions. Otherwise, the day must be a weekend, and so
only the infprob and play advance functions are returned.
Run metawards using this new iterator and see what happens;
metawards -d lurgy3 --additional ExtraSeedsLondon.dat --iterator week
metawards-plot -i output/results.csv.bz2 --format jpg --dpi 150
You should see something similar to this;
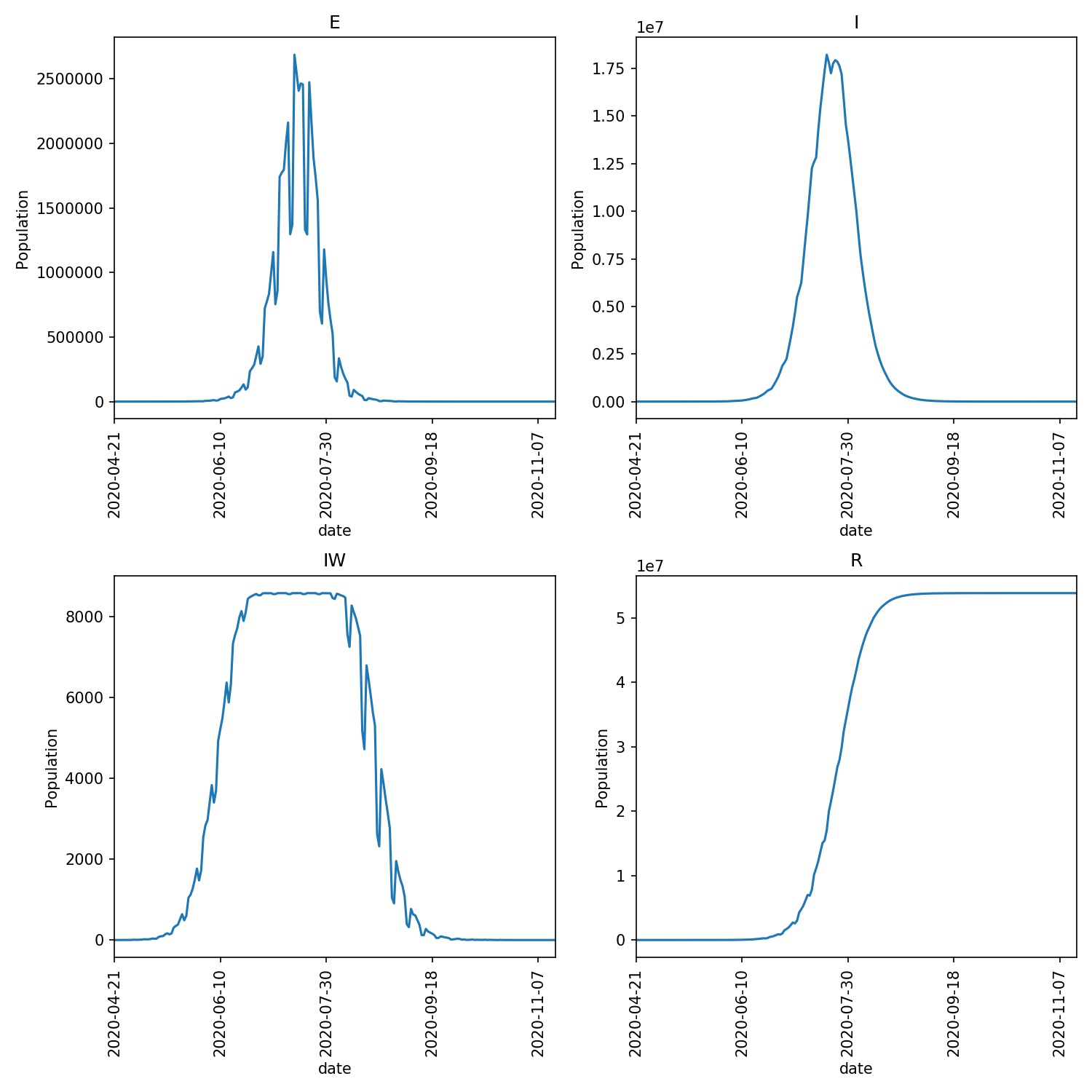
There is a significant spread in the infection during weekdays, but then this growth falls back at weekends.
Note
This “week” iterator is so important that it is supplied
as the metawards.iterators.iterate_working_week()
iterator. You can use this via the command line option
--iterator iterate_working_week. Similarly there
is metawards.iterators.iterate_weekday() function
to iterate as a weekday only, and
metawards.iterators.iterate_weekend() to iterate
as weekends only.
Note
By default the outbreak is modelled to start from today.
You can control the start date using the --start-date
command line option.
Changing iterators with stage
This method of modelling the weekend, while simple, is not correct. We have modelled the weekend as a time when only the players move and can be infected. The workers are ignored, meaning that this model assumes that the workers spend their weekends at home, not interacting with anyone else, and thus have zero risk of contracting an infection.
To model the weekend properly, we have to do something to advance the
workers. One option is to advance workers at the weekend in the same way
that we advance players. Because the data structure used to model
workers is different, we can’t just call the
advance_play() function on the workers.
Instead, metawards comes with
advance_work_to_play(). This advances the
workers as if they were players.
Using this, the iterate_week iterator could look like;
from metawards.iterators import advance_infprob, \
advance_work_to_play, \
advance_play
from metawards.utils import Console
def iterate_week(population, **kwargs):
date = population.date
Console.debug(f"Creating functions for {date}")
if date.weekday() < 5:
Console.debug("This is a weekday")
return [advance_infprob,
advance_fixed,
advance_play]
else:
Console.debug("This is a weekend")
return [advance_infprob,
advance_work_to_play,
advance_play]
However, this would also not be correct. The issue is that, as well as advancing the infection, the iterator is also responsible for calculating the force of infection (FOI) resulting from infected individuals. This is calculated during the “foi” stage of the day.
Each model day is divided into a series of stages;
initialise : used to initialise any variables that day
setup : used to set up any additional variables or infections
foi : used to calculate the FOI resulting from existing infections
infect : used to calculate and enact new infections
analyse : used to calculate / analyse the data from infections
In addition, for a model run, there is a finalise stage, which is called once at the end of a model run, at which all outputs from a model run are written to disk or a database. Then, for a collection of model runs, there is a summary stage which is called once at the end of all model runs, to calculate and write out summary statistics from all runs.
By default, a custom iterator will only specify the advance functions
that are used for the infect stage. The advance functions used for
other stages are supplied by
iterate_default(). By default, the
advance_foi() function is used to
calculate the FOI. This assumes that all workers behave like
workers, and all players behave like players. It does not work
when we use advance_foi_work_to_play(),
because this makes the workers behave like players.
We thus need to use the advance_foi_work_to_play()
function instead. To do this, we need to tell metawards to use that
function in the foi stage. We can control which stage our iterator
operates by passing in the stage argument. For example;
from metawards.iterators import advance_infprob, \
advance_work_to_play, \
advance_play, \
advance_foi, \
advance_foi_work_to_play, \
advance_recovery
from metawards.utils import Console
def iterate_week(stage, population, **kwargs):
date = population.date
Console.debug(f"Creating functions for {date}")
is_weekend = date.weekday() < 5
if is_weekend:
Console.debug("This is a weekend")
if stage == "foi":
return [advance_foi_work_to_play,
advance_recovery]
elif stage == "infect":
return [advance_infprob,
advance_work_to_play,
advance_play]
else:
return iterator_default(stage=stage, **kwargs)
else:
Console.debug("This is a weekday")
if stage == "foi":
return [advance_foi,
advance_recovery]
elif stage == "infect:
return [advance_infprob,
advance_fixed,
advance_play]
else:
return iterator_default(stage=stage, **kwargs)
Note
advance_recovery() is another advance
function that must be returned at the foi stage. This advance
function is used to advance infected individuals along
the stages of the disease (e.g. E to I to R).
Note
iterate_default() returns the default
set of advance functions for each stage. It makes sense
to call this for the stages that you are not explicitly
handling in your iterator, e.g.
return iterate_default(stage=stage, **kwargs) will return
the default advance functions for the specified stage.
With those changes, the iterate_week iterator would work as a model where all workers become players at the weekends.
To make things easier, metawards provides a built-in
iterate_weekend() iterator for
iterating a weekend day, plus a
iterate_working_week() iterator that
will use iterate_default() for weekdays,
and iterate_weekend() for weekends.
Use these if you want to model a working week where workers
behave like players at the weekend.